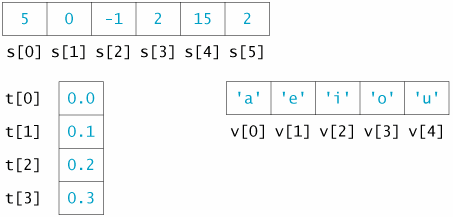

int s[6]={5,0,-1,2,15,2};
char v[5]={'a','e','i','o','u'};
double t[4]={0.0,0.1,0.2,0.3};
If the initializing sequence is shorter than the array,
then the rest of the values are initialized to zero.
int s[100]={1,2}; // same as {1,2,0,0,0....
int z[100]={0}; // z initialized to all 0's
If an array is specified without a size, but with an initialization
sequence, the size is defined to be equal to the number of values in the
sequence.
int s[]={5,0,-1,2,15,2}; // same as: int s[6]={5,0,-1,2,15,2};
double t[]={0.0,0.1,0.2,0.3}; // same as: double t[4]={0.0,0.1,0.2,0.3};
Using a for loop to traverse an array:
int k; // Declare variables double g[21]; ... for (k=0; k<21; ++k) // Initialize the array g g[k] = k*0.5;Again, using a function:
void init( double x[], int n) // Initialize an array
{
int k;
for (k=0; k<n; ++k)
x[k] = k*0.5;
}
... in main:
double g[21];
init( g, 21);
int M;
// ... set M to some value ...
double q[M]; // variable-size array, can not initialize with literal list, e.g. {1,2,3}
init( q, M); // this works
#include <stdio.h>
void aprint( int a[], int n) // print an integer array of any size (using size n)
{
for( int i = 0; i < n; ++i) printf( " %i", a[i]);
putchar('\n');
}
void add6( int a[], int n) // add 6 to each element of an integer array
{
for( int i = 0; i < n; ++i) a[i] += 6;
}
int main(void)
{
int x[10]={0,1,2}; // x[0], x[1], ..., x[9]
aprint( x, 10);
for( int i = 0; i<10; ++i) x[i] = i;
aprint( x, 10); // print all 10 values of x
aprint( x, 5); // print first 5 values of x
add6( x, 4); // add 6 to first 4 elements of x
aprint( x, 10); // print all 10 values of x
aprint( x+3, 5); // print 5 values of x starting with offset 3
return 0;
}
Output:
0 1 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 6 7 8 9 4 5 6 7 8 9 9 4 5 6 7
chapter5_2.c
/*-------------------------------------------------------------*/
/* This function returns the maximum value in an array x */
/* with n elements. */
double max(double x[],int n)
{
/* Declare variables. */
int k;
double max_x;
/* Determine maximum value in the array. */
max_x = x[0];
for (k=1; k<=n-1; k++)
if (x[k] > max_x)
max_x = x[k];
/* Return maximum value. */
return max_x;
}
Also see functions in chapter5_5.c