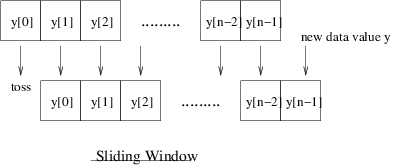
Consider a 3-point moving average using three variables for a sliding window:
double y0, y1 = 0, y2 = 0;
loop over incoming data d
y0 = y1; y1 = y2; // slide window
y2 = d; // store new value
z = (y0+y1+y2)/3.0; // compute average
We can change the code to use an array instead of three variables:
double y[3] = { 0 };
loop over incoming data d
y[0] = y[1]; y[1] = y[2]; // slide window
y[2] = d; // store new value
z = (y[0]+y[1]+y[2])/3.0; // compute average
then generalize to an array of size n:
for( i = 0; i < n-1; ++i) // slide window
y[i] = y[i+1];
y[n-1] = d; // store new value

Each time the array is shifted, the original value of y[0] is lost and
the new data value is stored in y[n-1].