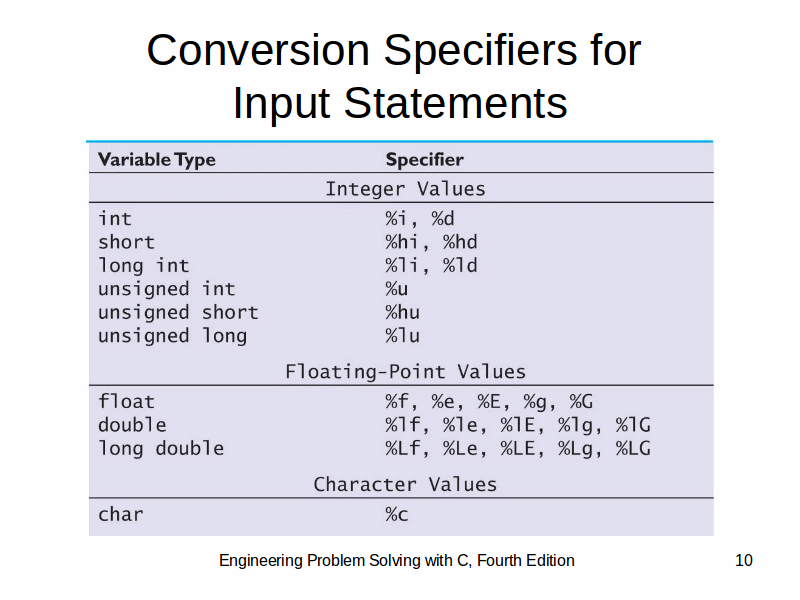
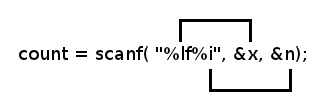scanf example:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main( void)
{
int n, count;
double x, y;
count = scanf( "%lf%i", &x, &n);
printf( "count = %i\n", count);
y = pow( x, n);
printf( "x = %g, n = %i, y = %g\n", x, n, y);
return 0;
}
& address-of operator, e.g.
&x could be 100, &n could be 108:

sample runs:
input output
----- ------
count = -1
x = 1.40178e-307, n = 134514009, y = 0
abc count = 0
x = 7.6521e-308, n = 134514009, y = 0
1.1 abc count = 1
x = 1.1, n = 134514009, y = inf
1.1 2 count = 2
x = 1.1, n = 2, y = 1.21
Each % format acts like a placeholder for a value to be read:
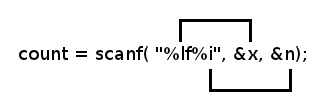
primary formats:
char %c
int %i
double %lf
Table 2.7, page 47: