In this Section we present two sets of
simulation results to
show the effect that the multiuser PSP and RSSE
algorithms presented in this paper have on the
performance of MLSE based estimation. For all results,
the number of users was K=2, the number of chips per
symbol was N=4, the channels each had FIR length M=3,
the Gauss-Markov factor was
![]() ,
and
the Gauss-Markov model noise covariance was
,
and
the Gauss-Markov model noise covariance was
![]() .
For each simulation
trial a set of the users' chip impulse responses were
generated using the Gauss-Markov model.
User 1 was 10dB stronger than user 2.
.
For each simulation
trial a set of the users' chip impulse responses were
generated using the Gauss-Markov model.
User 1 was 10dB stronger than user 2.
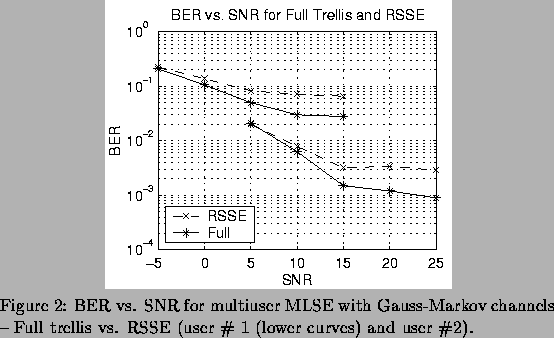
For the first set of results, a full trellis was used (no RSSE), and PSP was compared to the exhaustive search solutions, that provides the optimum MLSE. The number of symbols per simulation was n=5, and 2000 trials per SNR were run. Figure 1 shows results. Although PSP with L=1 path saved per trellis state (i.e. standard Viterbi) performed significantly worse than exact MLSE, performance was close to exact MLSE for L=3. We have found L=3 to be adequate in all simulations we performed.
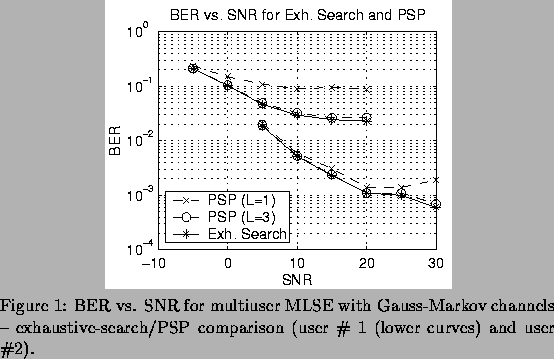
The second set of results, shown in Figure 2, compare RSSE to full trellis. For both, L=3. The number of symbols per simulation was n=5, and 2000 trials per SNR were run. Figure 2 illustrates that RSSE provides results comparable to full trellis.