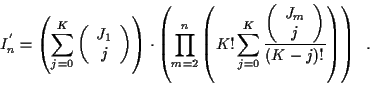Next: MAP Based Track Estimation
Up: Multitarget Tracking Problem
Previous: Hypothesized Tracks
Now consider a set of K tracks. Assume tracks can not share detections,
and again assume missed detections are
possible3.
It can be shown that the number of hypothesized track sets
is4
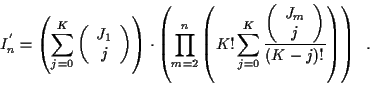 |
(4) |
Let the ith hypothesized K-track set be represented as
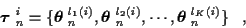 |
(5) |
where the superscript lk (i) denotes the kth track of the ithtrack set.
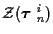 will be used to denote
the measurement data associated with the ith K-track set.
Multiple Hypothesis Tracking (MHT) algorithms aim to determine at time nthe best from the In' hypothesized track sets.
will be used to denote
the measurement data associated with the ith K-track set.
Multiple Hypothesis Tracking (MHT) algorithms aim to determine at time nthe best from the In' hypothesized track sets.
Rick Perry
2000-05-06