


Next: Additional Hypothesis Merging and
Up: A New Pruning/Merging Algorithm
Previous: Trellis Diagram Formulation
The multitarget tracking algorithm we propose incorporates the list Viterbi
algorithm, along with the K-track trellis formulation of the multitarget
tracking problem [18], and MAP cost computation based on Kalman
filter innovations and prior track set probabilities. The algorithm
determines a list of L feasible K-tracks sets as a list of L paths
through the measurement set trellis.
Algorithm
- 1)
- Setup:
For each time
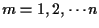 ,
allocate arrays of size Mm-by-L for the
predecessor state indices, predecessor state L-best indices,
permutation number of the current state measurement indices to track
associations, and current total minimum negative log costs. Allocate
Kalman filters for each track in each L-best sets of tracks for each state.
,
allocate arrays of size Mm-by-L for the
predecessor state indices, predecessor state L-best indices,
permutation number of the current state measurement indices to track
associations, and current total minimum negative log costs. Allocate
Kalman filters for each track in each L-best sets of tracks for each state.
- 2)
- Initialization:
For
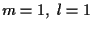 ,
the current costs are set using
(17) for the a priori
probabilities, since no Kalman filter innovations are available
initially. The Kalman filters are initialized using the available
measurements for time m=1, and using predicted values for time m=2.
,
the current costs are set using
(17) for the a priori
probabilities, since no Kalman filter innovations are available
initially. The Kalman filters are initialized using the available
measurements for time m=1, and using predicted values for time m=2.
- 3)
- Iteration:
For each time
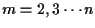 ,
and for each state
,
and for each state
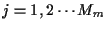
- 3.1)
- Add incremental costs (13)
from the L-best of each previous state to the total previous costs, and
temporarily store these hypothesized new costs.
- 3.2)
- Select the L-best of the hypothesized new costs and update the
associated Kalman filters.
- 4)
- Results: Output the final L-best sets of tracks.
Although the algorithm is described above in block form, it is
time-sequential, and at any time during the iterations can produce current
estimates of the best tracks.



Next: Additional Hypothesis Merging and
Up: A New Pruning/Merging Algorithm
Previous: Trellis Diagram Formulation
Rick Perry
2000-05-06