


Next: Time Varying Number-of-Track Estimation
Up: MHT Viterbi Algorithm for
Previous: The MHT Viterbi Algorithm
Exact implementation of either the joint
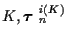 estimator or the marginalized K estimator requires calculation of costs
for all hypothesized track sets
estimator or the marginalized K estimator requires calculation of costs
for all hypothesized track sets
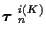 for all
possible K. This in not practical. Alternatively we use the MHT Viterbi
algorithm to prune and merge.
Assume that Kmax is the largest possible value of K.
For the trellis and algorithm described in Subsections 4.1 and 4.2 above,
consider a trellis for a fixed value of Kmax.
Embedded in the branch and path costs of this trellis are all of the costs
required to evaluate all K-track set hypotheses for all
for all
possible K. This in not practical. Alternatively we use the MHT Viterbi
algorithm to prune and merge.
Assume that Kmax is the largest possible value of K.
For the trellis and algorithm described in Subsections 4.1 and 4.2 above,
consider a trellis for a fixed value of Kmax.
Embedded in the branch and path costs of this trellis are all of the costs
required to evaluate all K-track set hypotheses for all
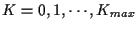 .
So, we can use this single trellis structure
to solve the K estimation problem. The number-of-tracks estimator
we have implemented:
.
So, we can use this single trellis structure
to solve the K estimation problem. The number-of-tracks estimator
we have implemented:
- 1)
- Constructs the trellis for K=Kmax.
- 2)
- Employs the Viterbi MHT algorithm to prune hypothesized track sets.
- 3)
- Uses track costs stored in the trellis to generate track set costs
for
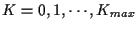 .
.
- 4)
- Estimates K using (a merged/pruned version of) either
(14) or (15).
Rick Perry
2000-03-26